Crossed roller bearing overview | BRS Bearing
Crossed roller bearings are with the characteristic of small size, high rotation precision, strong deformation resistance, high loading capacity, and flexible structural design. They are widely used in joint and rotating parts of industrial robots, CNC rotary tables, indexing tables, measuring instruments, machine tools, medical equipment, optical telescope, radars, etc. Now let's give a quick crossed roller bearing overview of its structure, features, and types.
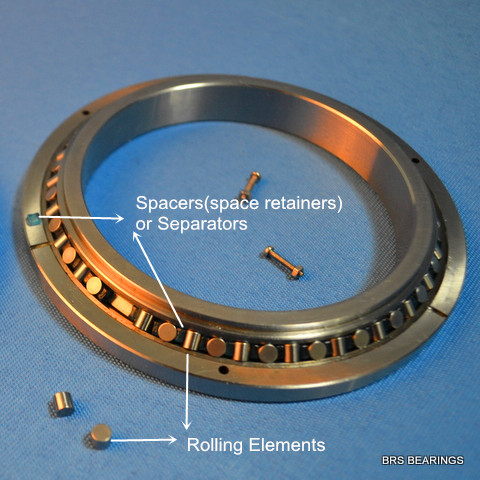
The rolling elements of crossed roller bearings are generally cylindrical rollers or tapered rollers, which are arranged crosswise in a V-shaped groove. So these bearing can simultaneously receive radial, axial, and moment loads. The nylon spacers(separators) are placed between the alternate rollers, which can prevent rollers from skewing. Therefore the friction between rollers is reduced, which can prevent the bearings' rotation torque from increasing.
Crossed roller bearing overview - Advantages
- Crossed roller bearings can be assembled in all directions of the spindle.
- It can withstand radial and axial loads at the same time. So one cross roller ring can replace two common ball/roller bearings. This will simplify the structure of the device and reducing the weight of the mechanism.
- Cross roller bearings have low grease consumption due to high rotation efficiency and low heat dissipation.
- Extremely high rotation accuracy and high overturning moment can be achieved with negative clearance.
- High rigidity, 3-4 times robust than traditional bearings.
- With high load-carrying capacity, the roller is in line contact with the raceway, so it can withstand higher loads.
Crossed roller bearings types
- Integrated inner ring with split outer ring type (like THK RA/RB, IKO CRB)
- Split inner ring with integrated outer ring type(such as THK RE)
- Integrated inner and outer ring type without mounting holes(like IKO CRBH)
- Mounting holed type solid one-piece inner and outer ring(like THK RU, IKO CRBF)
To determine cross roller bearings' structure, need to confirm the rotation part of the mechanism.
If it's outer ring rotation, then need to choose the split inner ring with integrated outer ring type.
And similarly, a split outer ring with an integrated inner ring type is suited for inner ring rotation.
If both the inner ring and outer ring need to rotate, then the solid one-piece inner and outer ring type will be a better choice. This article will help you select crossed roller bearings step by step.
Conclusion
A crossed roller bearing is designed to meet the requirements of high precision applications. Its running accuracy includes several levels, such as P5/P4/P2/VSP. If you are interested in BRS bearing products' performance on the rotation precision, below is a video showing the VSP grade bearing product's run-out test.

